What Are the Stages of Layer-2 Development?

With the rapid development of Layer-2 solutions, it can be confusing to categorize and rank these networks in your portfolio. Today, we'll explore the concept of Stages, a reference scale introduced by Vitalik Buterin in a blog post in November 2022, to better understand the development phases of Layer-2 solutions.

Why Do Layer-2s Have Stages?
The concept of development Stages for Rollups, a subset of Layer-2 solutions, was introduced to help gauge the progress of a Layer-2 network towards achieving Ethereum-like security and functionality.
Reaching the "basic rollup scaling" milestone in my roadmap diagram.
— vitalik.eth (@VitalikButerin) December 31, 2022
That means:
* EIP-4844 rolled out
* Rollups partially taking off training wheels, at least to "stage 1" as described here https://t.co/qNQonDQkzG pic.twitter.com/7HePctWw1l
- Rollup Stage Assessment: Stage assessment helps estimate how close a Rollup is to Ethereum's functionality and security.
- DApp Development: Understanding a Rollup's stage helps developers avoid technical mishaps and asset lockouts when building applications.
- User Withdrawal Process: It clarifies how user withdrawals from Layer-2 to Layer-1 will be handled.
- Security Evaluation: It assesses the network's decentralization and potential attack risks.
- Development Incentive: It motivates Rollup projects to improve and sets a benchmark for transitioning to the Ethereum upgrade "The Surge."
The Specific Stages of Layer-2
There are three main stages, each with increasing levels of security and functionality, numbered from 0 to 2.
Stage 0
- Rollup Nodes: At this stage, Rollup nodes process transactions and interact with Layer-1 for data storage and retrieval.
- User Withdrawals: Users need mechanisms to request withdrawals, preventing unilateral locking or freezing of assets by Rollup operators.
A Stage 0️⃣ rollup is essentially run by the operators. We diverge from Vitalik's proposal by not requiring independent exit mechanisms at this stage, as instant upgrades or absent state validation negate their security benefits.
— L2BEAT 💗 (@l2beat) June 19, 2023
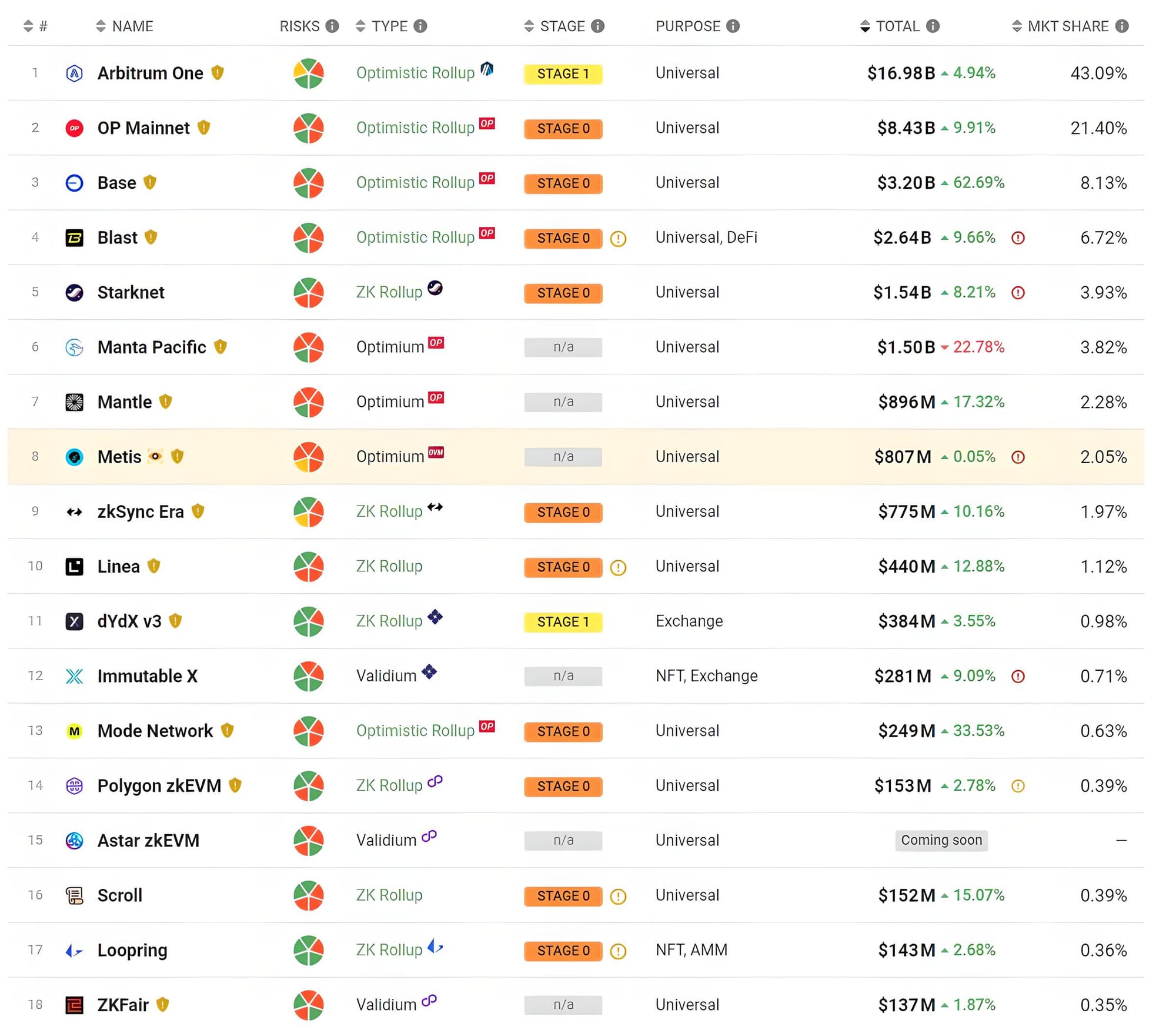
Examples: OP Mainnet (Optimism), Base, Blast, Starknet, zkSync Era, Linea, Scroll.
These networks, despite their significant TVL, are still at Stage 0 due to the lack of a verified proof system that reduces reliance on the project itself.
Stage 1
- Proof System: At this stage, a verifiable proof system (Fraud Proof or Validity Proof) is implemented. This system ensures user trust in transaction validity.
- Multisig Governance: A Security Council (multisig) can intervene in case of proof validation errors. Upgrades require a 7-day delay after multisig approval.
Examples: Arbitrum, dYdX, zkSync Lite.
Stage 2
- Smart Contract Governance: The network operates autonomously based on smart contracts. No single entity can alter the network's operations if no errors occur.
- Proof System Autonomy: The proof system operates independently of any entity, including the Security Council. Upgrades need a 30-day delay after approval.
A Stage 0️⃣ rollup is essentially run by the operators. We diverge from Vitalik's proposal by not requiring independent exit mechanisms at this stage, as instant upgrades or absent state validation negate their security benefits.
— L2BEAT 💗 (@l2beat) June 19, 2023
Examples: DeGate, Fuel.
Tracking Layer-2 Stages
You can follow the development stages of Layer-2 networks on platforms like L2Beat or by reading the blogs and announcements from Layer-2 projects themselves.
Conclusion
Understanding the development stages of Layer-2 solutions, especially Rollups, provides a new reference scale for evaluating their progress and security. This knowledge helps in making informed decisions about which Layer-2 solutions to support and invest in.





