What is Restaking? A New Solution to Ethereum's Decentralization Dilemma

As the Ethereum community expresses concerns about the risks of "centralization of power" among a select group of projects, "Restaking" has emerged as a keyword of significant interest and is anticipated to offer a fitting solution. So, what exactly is Restaking? Let's dive into the details below.

The Restaking Challenge
First, let's explore why the concept of Restaking has gained attention recently.
At the SBC 2022 conference, EigenLayer's Sreeram Kannan raised concerns about decentralization in relation to the Mev-Boost application network.
Read more: [What is Mev-Boost? What Will Happen to the MEV Market After The Merge?]
Given these limitations, Restaking has emerged as a solution that penalizes (slashes) nodes exhibiting malicious behavior while ensuring they continue to benefit from MEV by using Mev-Boost's Relayer.
How Restaking Works
As there isn't much documentation or many projects implementing Restaking yet, this article will focus on EigenLayer (a project that has been receiving significant attention recently).
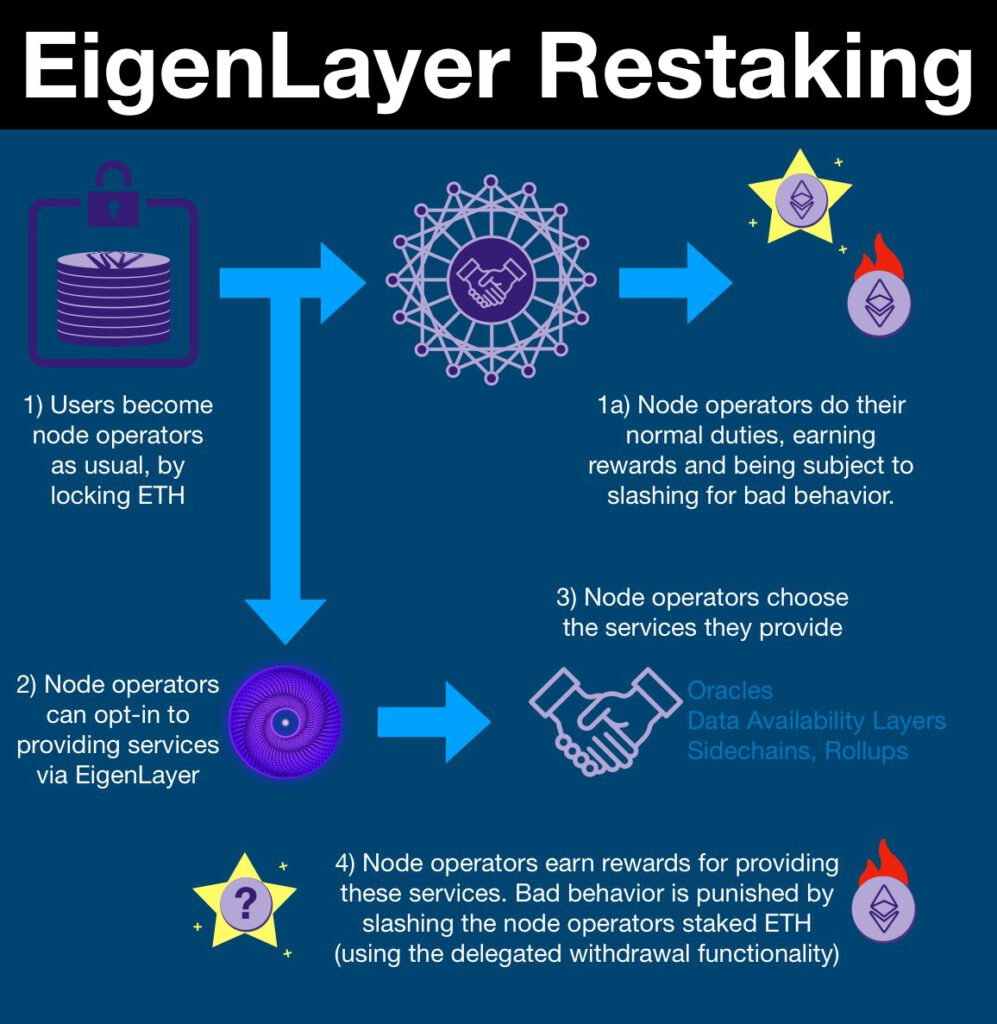
Here’s a simplified model of how Restaking operates:
- Stake ETH on the Chain: Users stake ETH on the Ethereum chain as usual. Validators then use this staked ETH to maintain network operations.
- Delegate ETH to EigenLayer Contract: Validators additionally delegate their ETH to EigenLayer's contract. They interact to select tasks to perform in the next step. Thus, the initial ETH can be applied to multiple security tasks simultaneously.
- Perform Tasks: These tasks can include Oracle services, Data Availability, and the deployment of Sidechains or Rollups.
- Earn Rewards and Face Penalties: Nodes receive rewards for completing tasks. However, if they engage in fraudulent activities, they face penalties (referred to as "slashing").
In summary, Restaking can be understood as an application layer that decentralizes validators while repurposing staked Ethereum for additional security functions.
Impact
- Reducing Dependence on Mev-Boost: Restaking helps mitigate risks associated with relying on Flashbots' Mev-Boost. Since much of the processing from Builder to Relayer to Proposer/Validator happens off-chain, a slashing layer is crucial for managing potential fraudulent behavior by validators.
- Balancing MEV Profits and Network Security: Restaking enables Validators to balance MEV profitability with overall network security. Validators must:
- Stake in the Restaking platform to face penalties if they engage in fraud.
- Commit to honest behavior in their interactions with Mev-Boost's Relay.
- Enhancing Capital Efficiency: Staked Ethereum can be reused, thereby increasing capital efficiency.
- Stimulating ETH Demand: This mechanism could drive additional demand for ETH to stake on the network.
Risks
- Effectiveness of the New Model: The effectiveness of this new model remains unproven in the market, and the capabilities of the involved teams are still uncertain.
- Centralization Concerns: Despite the potential benefits, concerns about centralization persist. Platforms like Lido Finance and Flashbots have already significantly influenced blockchain operations, raising fears of power concentration. If Restaking is not properly designed, it could introduce new centralization risks.
- Security Risks: Although the risk of misuse of user ETH is mitigated by smart contracts managing Restaking, technical implementation errors could lead to catastrophic consequences for the entire blockchain.
Conclusion
This overview provides fundamental insights into Restaking. We hope this information helps you gain a better understanding of the potential market developments ahead.
Note: All content is for informational purposes only and should not be considered investment advice.
Goodbye for now, and see you in the next article!





